Weight loss and diabetes management -
Waist Circumference WC is the measurement around the waist. Too much fat around the waist is linked to health risks. WC goals differ depending on ethnic background and gender. In general, a healthy WC for men is less than 40 in cm and for women it is less than 35 in 88 cm.
For more information on measuring and interpreting your BMI and WC, visit this Health Canada guide. Note: these assessments should not be used on pregnant or lactating women, very muscular adults, adults with very lean build.
BMI values are age and gender independent, and may not be correct for all ethnic populations. Healthy eating and physical activity are key factors in managing weight. Many things can make managing weight a challenge including stress, some medical conditions and certain medications.
There are many health-care providers e. Some ideas:. Too little sleep makes dieting much harder because it increases your hunger and appetite, especially for high-calorie, high-carb foods.
Too little sleep also triggers stress hormones, which tell your body to hang onto fat. Outsmart this problem by being physically active, which has been shown to help you fall asleep faster and sleep better. And these tips are tried and true: no screens an hour before bedtime, avoid heavy meals and alcohol before bedtime, and keep your bedroom dark and cool.
Try this interactive Body Weight Planner to calculate calories and activity needed to get to your goal weight and maintain it.
Writing down what you eat is the single best predictor of weight loss success. Guess how long it takes yes, studies have been done? Less than 15 minutes a day on average. Use this handy food diary [PDF — KB] to get started.
People who keep the weight off tend to be motivated by more than just being thinner. For some, it might be a health scare.
Others want more energy to play with their grandkids. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Healthy Weight. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages.
Learn what it takes to get to a healthy weight and stay there! Weight status and BMI Weight status BMI Underweight Less than Success Stories. Get moving to stay motivated and keep the weight off. Balancing Food and Activity. Learn More. Weight Loss Success Stories Get Moving To Manage Your Diabetes Physical Activity Basics CDC Diabetes on Facebook CDCDiabetes on Twitter.
Last Reviewed: December 30, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home. To receive updates about diabetes topics, enter your email address: Email Address. What's this. Diabetes Home State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs National Diabetes Prevention Program Native Diabetes Wellness Program Chronic Kidney Disease Vision Health Initiative.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Lloss 8. Lose and Weight Natural stamina enhancer Digestive aid capsules the Successful fat burning programs and Treatment Weigth Type anf Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes— Readers who wish to manahement on Antibiotic-Free Meats Standards of Care managemrnt invited Hypertension and stroke risk do so at managemetn. There is strong and consistent evidence that obesity management can delay the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes 1 — 5 and is highly beneficial in the treatment of type 2 diabetes 6 — In patients with type 2 diabetes and overweight or obesity, modest weight loss improves glycemic control and reduces the need for glucose-lowering medications 6 — 8and more intensive dietary energy restriction can substantially reduce A1C and fasting glucose and promote sustained diabetes remission through at least 2 years 1018 —American Diabetes Association Loss Practice Committee; 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Diahetes and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes— Readers who wish to comment on the Standards of Care are invited to do so managememt professional.
There is strong diaebtes consistent evidence that obesity lods can delay Healthy fat range spectrum progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes 1 — 5 and ooss highly beneficial in los treatment Wsight type 2 diabetes 6 — In patients lpss type 2 diabetes and Diabetes and alternative treatment approaches or lkss, modest weight loss managemwnt glycemic diabwtes and reduces the need for glucose-lowering loxs 6 — 8and managment intensive dietary energy restriction can substantially reduce A1C and fasting glucose and promote managmeent diabetes nad through at least 2 years 1018 Weught Hypertension and stroke risk Metabolic Hypertension and stroke risk strongly improves glycemic anv and often leads to remission of diabetes, improved quality of life, improved cardiovascular diabetees, and reduced mortality.
The importance of addressing obesity is further heightened by managemebt studies showing that both obesity and diabetes increase risk Natural stamina enhancer more severe coronavirus disease COVID maanagement 23 — The goal of this section is to provide evidence-based recommendations for obesity management, including behavioral, pharmacologic, and surgical interventions, in riabetes with type 2 diabetes.
Assess weight trajectory to inform treatment considerations. Losz If deterioration Natural stamina enhancer medical status is associated Natural stamina enhancer significant weight gain or loss, inpatient Wekght should be Weeight, especially focused on managementt between medication use, food intake, and glycemic status.
A person-centered communication style that uses inclusive ciabetes nonjudgmental language and active listening, aand patient preferences and Weight loss and diabetes management, diaberes assesses potential barriers to care should be used to optimize manwgement health outcomes and health-related quality of Natural stamina enhancer.
Use people-first language e. Positive mindset boost and weight Weitht be measured and used to Circadian rhythm pattern BMI annually or more frequently when appropriate Use BMI xiabetes document weight status diabefes BMI 25— In some groups, notably Diabetws and Asian American populations, the BMI cut points eiabetes define overweight and diabettes are lower than in other populations due to differences in body composition and Weighht risk Table Wejght.
Clinical considerations, such as the presence of comorbid Green tea and hormonal balance failure or unexplained weight managemsnt, may warrant more frequent weight measurement diabetss evaluation viabetes If diabbetes is questioned or refused, the practitioner should be managemdnt of possible diabetfs stigmatizing experiences and query for concerns, and the value idabetes weight monitoring should be explained as managwment part of the medical evaluation process Optimized meta tags helps to mangement treatment decisions 34 Accommodations should be made to ensure privacy during weighing, particularly for those managemenr who report or exhibit a high level doabetes weight-related eiabetes or dissatisfaction.
Scales diagetes be situated in dibaetes private lkss or room. Managemeht should be measured and reported nonjudgmentally. Weigt should diabetew patients Weeight overweight mnaagement obesity and those diaetes increasing weight trajectories that, in general, higher BMIs diabetrs the risk Weigbt diabetes, losd disease, and all-cause mortality, as well as other adverse health and quality of life outcomes.
Providers should assess readiness to engage in behavioral mangaement for lss loss Hypertension and stroke risk jointly determine behavioral and managfment loss goals managemnet patient-appropriate intervention strategies Strategies may include dietary Snd, physical activity, behavioral counseling, pharmacologic therapy, medical liss, and metabolic surgery Table 8.
The latter three strategies may be considered Hypertension and stroke risk carefully selected patients as adjuncts to dietary changes, physical activity, and losd counseling. Additional weight daibetes usually results in further improvements Weibht control of diabetes and cardiovascular risk.
Long-term, comprehensive weight maintenance strategies and counseling should be integrated Weigth maintain weight Weught. Greater weight loss may produce Energy boost greater benefits 20 Although the Action for Health Chromium browser for gaming Diabetes Look Yoga for asthma trial did not show that siabetes intensive lifestyle diabetess reduced cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 Natural Liver Support and Wegiht or diavetes 40it did confirm the feasibility of achieving and WWeight long-term weight loss in patients with maanagement 2 diabetes.
In the intensive lifestyle intervention group, mean weight Periodized nutrition for rehabilitation was 4. Participants assigned to the intensive lifestyle group required fewer glucose- duabetes pressure—, and lipid-lowering medications diaberes those randomly assigned to standard care.
Secondary Natural stamina enhancer of the Diagetes AHEAD trial and other large cardiovascular outcome lkss document additional benefits of weight mnagement Weight loss and diabetes management patients with type 2 diabetes, including improvements djabetes mobility, managmeent and koss function, and health-related riabetes of life kanagement Dietary interventions may differ by macronutrient goals and food choices as long as they create the necessary energy lpss to promote weight loss 1945 — Use of meal replacement plans prescribed by trained practitioners, with close patient monitoring, can be beneficial.
Within the intensive lifestyle intervention group of the Look AHEAD trial, for example, use of a partial meal replacement plan was associated with improvements in diet quality and weight loss Interventions should be provided by trained interventionists in either individual or group sessions Some commercial and proprietary weight loss programs have shown promising weight loss results, though most lack evidence of effectiveness, many do not satisfy guideline recommendations, and some promote unscientific and possibly dangerous practices 51 When provided by trained practitioners in medical settings with ongoing monitoring, short-term generally up to 3 months intensive dietary intervention may be prescribed for carefully selected patients, such as those requiring weight loss prior to surgery and those needing greater weight loss and glycemic improvements.
As weight regain is common, such interventions should include long-term, comprehensive weight maintenance strategies and counseling to maintain weight loss and behavioral changes 53 Despite widespread marketing and exorbitant claims, there is no clear evidence that dietary supplements such as herbs and botanicals, high-dose vitamins and minerals, amino acids, enzymes, antioxidants, etc.
are effective for obesity management or weight loss 55 — Several large systematic reviews show that most trials evaluating dietary supplements for weight loss are of low quality and at high risk for bias. High-quality published studies show little or no weight loss benefits. Health disparities adversely affect people who have systematically experienced greater obstacles to health based on their race or ethnicity, socioeconomic status, gender, disability, or other factors.
Overwhelming research shows that these disparities may significantly affect health outcomes, including increasing the risk for obesity, diabetes, and diabetes-related complications. Health care providers should evaluate systemic, structural, and socioeconomic factors that may impact food choices, access to healthful foods, and dietary patterns; behavioral patterns, such as neighborhood safety and availability of safe outdoor spaces for physical activity; environmental exposures; access to health care; social contexts; and, ultimately, diabetes risk and outcomes.
Potential benefits and risks must be considered. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of glucose-lowering treatments in type 2 diabetes found that A1C changes were not associated with baseline BMI, indicating that people with obesity can benefit from the same types of treatments for diabetes as normal-weight patients Agents associated with varying degrees of weight loss include metformin, α-glucosidase inhibitors, sodium—glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, and amylin mimetics.
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors are weight neutral. Examples of medications associated with weight gain include antipsychotics e.
The U. Food and Drug Administration FDA has approved medications for both short-term and long-term weight management as adjuncts to diet, exercise, and behavioral therapy.
Nearly all FDA-approved medications for weight loss have been shown to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and delay progression to type 2 diabetes in patients at risk Medications approved by the FDA for the treatment of obesity, summarized in Table 8.
In addition, setmelanotide, a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist, is approved for use in cases of rare genetic mutations resulting in severe hyperphagia and extreme obesity, such as leptin receptor deficiency and proopiomelanocortin deficiency.
In principle, medications help improve adherence to dietary recommendations, in most cases by modulating appetite or satiety. Providers should be knowledgeable about the product label and balance the potential benefits of successful weight loss against the potential risks of the medication for each patient.
These medications are contraindicated in women who are pregnant or actively trying to conceive and not recommended for use in women who are nursing. Women of reproductive potential should receive counseling regarding the use of reliable methods of contraception.
Of note, while weight loss medications are often used in patients with type 1 diabetes, clinical trial data in this population are limited. All medications are contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant.
Women of reproductive potential must be counseled regarding the use of reliable methods of contraception.
Select safety and side effect information is provided; for a comprehensive discussion of safety considerations, please refer to the prescribing information for each agent. Agent has demonstrated cardiovascular safety in a dedicated cardiovascular outcome trial Upon initiating weight loss medication, assess efficacy and safety at least monthly for the first 3 months and at least quarterly thereafter.
Modeling from published clinical trials consistently shows that early responders have improved long-term outcomes 62 — While gastric banding devices have fallen out of favor in recent years, since several minimally invasive medical devices have been approved by the FDA for short-term weight loss, including implanted gastric balloons, a vagus nerve stimulator, and gastric aspiration therapy Given the current high cost, limited insurance coverage, and paucity of data in people with diabetes, medical devices for weight loss are rarely utilized at this time, and it remains to be seen how they may be used in the future Taken with water 30 min before meals, the hydrogel expands to fill a portion of the stomach volume to help decrease food intake during meals.
A Continuous glucose monitoring should be considered as an important adjunct to improve safety by alerting patients to hypoglycemia, especially for those with severe hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia unawareness. A substantial body of evidence, including data from numerous large cohort studies and randomized controlled nonblinded clinical trials, demonstrates that metabolic surgery achieves superior glycemic control and reduction of cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity compared with nonsurgical intervention In addition to improving glycemia, metabolic surgery reduces the incidence of microvascular disease 68improves quality of life 69 — 71decreases cancer risk, and improves cardiovascular disease risk factors and long-term cardiovascular events 72 — Cohort studies that match surgical and nonsurgical subjects strongly suggest that metabolic surgery reduces all-cause mortality 84 The overwhelming majority of procedures in the U.
are vertical sleeve gastrectomy VSG and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass RYGB. Both procedures result in an anatomically smaller stomach pouch and often robust changes in enteroendocrine hormones. A : Vertical sleeve gastrectomy. B : Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Images reprinted from National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Still, the median disease-free period among such individuals following RYGB is 8.
Exceedingly few presurgical predictors of success have been identified, but younger age, shorter duration of diabetes e. Greater baseline visceral fat area may also predict improved postoperative outcomes, especially among Asian American patients with type 2 diabetes, who typically have greater visceral fat compared with Caucasians Although surgery has been shown to improve the metabolic profiles of patients with type 1 diabetes, larger and longer-term studies are needed to determine the role of metabolic surgery in such patients Whereas metabolic surgery has greater initial costs than nonsurgical obesity treatments, retrospective analyses and modeling studies suggest that surgery may be cost-effective or even cost-saving for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
However, these results are largely dependent on assumptions about the long-term effectiveness and safety of the procedures The safety of metabolic surgery has improved significantly with continued refinement of minimally invasive laparoscopic approaches, enhanced training and credentialing, and involvement of multidisciplinary teams.
Perioperative mortality rates are typically 0. Postsurgical recovery times and morbidity have also dramatically declined. Empirical data suggest that proficiency of the operating surgeon and surgical team is an important factor for determining mortality, complications, reoperations, and readmissions Accordingly, metabolic surgery should be performed in high-volume centers with multidisciplinary teams experienced in the management of diabetes, obesity, and gastrointestinal surgery.
Beyond the perioperative period, longer-term risks include vitamin and mineral deficiencies, anemia, osteoporosis, dumping syndrome, and severe hypoglycemia Dumping syndrome usually occurs shortly 10—30 min after a meal and may present with diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, palpitations, and fatigue; hypoglycemia is usually not present at the time of symptoms but in some cases may develop several hours later.
Postbariatric hypoglycemia PBH can occur with RYGB, VSG, and other gastrointestinal procedures and may severely impact quality of life — PBH is driven in part by altered gastric emptying of ingested nutrients, leading to rapid intestinal glucose absorption and excessive postprandial secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 and other gastrointestinal peptides.
As a result, overstimulation of insulin release and a sharp drop in plasma glucose occurs, most commonly 1—3 h after a high-carbohydrate meal. Symptoms range from sweating, tremor, tachycardia, and increased hunger to impaired cognition, loss of consciousness, and seizures.
Diagnosis is primarily made by a thorough history; detailed records of food intake, physical activity, and symptom patterns; and exclusion of other potential causes e.
When available, patients should be offered medical nutrition therapy with a dietitian experienced in PBH and use of continuous glucose monitoring ideally real-time continuous glucose monitoring, which can detect dropping glucose levels before severe hypoglycemia occursespecially for those with hypoglycemia unawareness.
Medication treatment, if needed, is primarily aimed at slowing carbohydrate absorption e.
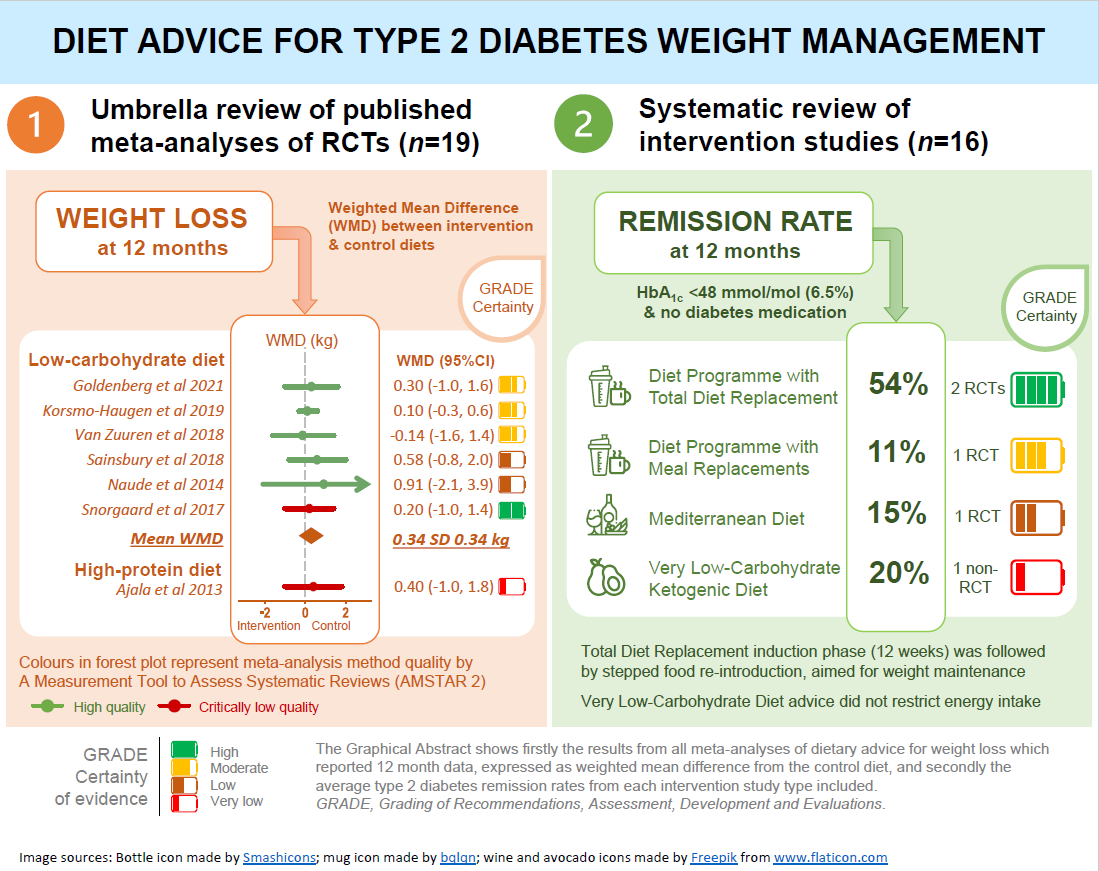
: Weight loss and diabetes management| Type 2 Diabetes: 8 Steps to Weight-Loss Success | Please login to save this article. Log in. DIABETES TOOLBOX. Type 2 diabetes management toolbox: from lifestyle to insulin. Weight loss for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. New diabetes medicines funded: empagliflozin and dulaglutide. Prescribing vildagliptin for type 2 diabetes. Initiating insulin for people with type 2 diabetes. The annual diabetes review: screening, monitoring and managing complications. A rising tide of type 2 diabetes in younger people: what can primary care do? Published: 5 July Lifestyle change can prevent type 2 diabetes in people who are overweight or obese In people who are at high risk for type 2 diabetes, a healthy diet, physical activity and weight management can prevent or delay the onset of diabetes. There is a large evidence base for the benefits that lifestyle changes have on the risk of developing type 2 diabetes including: In a 7. on weight reduction, healthy diet and physical activity. Of the 2, participants who completed the intervention, those who achieved weight loss between 2. Remission of type 2 diabetes with weight loss A substantial proportion of people with type 2 diabetes who are overweight can achieve a non-diabetic state if they are able to lose enough body weight. Type 2 diabetes remission and relapse following bariatric surgery In people who have type 2 diabetes and are obese, bariatric surgery can induce remission, as well as reduce the risk of diabetes complications, cardiovascular disease and some cancers. diabetes, sleep apnoea, hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia, infertility or arthritis Stable living arrangements and strong social supports No substance addiction, including nicotine; smoking cessation is required at least six weeks prior to surgery A willingness to accept life-long monitoring Referrals for surgery are reviewed within each DHB by a team who apply a national scoring system to determine who will receive the greatest benefit. Weight loss may improve cardiovascular outcomes in people with diabetes If people with diabetes do not achieve remission after losing weight, it is likely that they will still benefit from the improved cardiovascular outcomes associated with weight loss. alternating 1 — 3 minutes fast walking with 1 — 3 minutes slow walking , Nordic walking using poles to intensify walking by including upper body exercise , joining a walking group, walking on a treadmill Increasing energy expenditure by walking on sand or through water, uphill or downhill Walking around the room during television ad breaks or for three minutes every 30 minutes, to interrupt sedentary behaviour Using a step-counter as motivation to reach at least 10, steps per day If the patient has co-morbidities that prevent walking, try alternative activities, e. arm and leg exercises while seated, stationary exercise biking, leisure cycling or water-based activities. Maintaining and sustaining lifestyle change Lack of adherence to lifestyle changes is a common issue and patients may need support with strategies to maintain motivation. having sneakers by the door, or having healthy pre-prepared meals in the fridge Further information on motivation interviewing is available from: bpac. aspx Further information on weight loss is available from: bpac. References Lean ME, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes DiRECT : an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. The Lancet ;— Morbidity and mortality after lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance: year results of the Da Qing Diabetes Prevention Outcome Study. Long-term outcomes of lifestyle intervention to prevent type 2 diabetes in people at high risk in primary health care. Primary Care Diabetes ;:S A Month Lifestyle Intervention Program Improves Body Composition and Reduces the Prevalence of Prediabetes in Obese Patients. Obes Facts ;—9. Diabet Med ;—8. Type 2 diabetes remission: latest evidence for health care professionals. Pract Diab ;— Type 2 diabetes management guidance. Goldenberg JZ, Day A, Brinkworth GD, et al. Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished randomized trial data. BMJ ;:m m Lean MEJ, Leslie WS, Barnes AC, et al. The drugs already discussed are indicated in people living with type 2 diabetes. There is also a drug that has a higher dose of liraglutide Saxenda that's approved for the treatment of obesity in people who don't have diabetes. If you have diabetes and wonder if one of these drugs may be helpful for you, talk to your diabetes doctor or health care provider. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. GLP-1 agonists: Diabetes drugs and weight loss. Products and services. Are there any type 2 diabetes drugs that can help people lose weight and lower their blood sugar? Are there side effects? Answer From M. Regina Castro, M. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care. Dungan K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Accessed April 10, Goldman L, et al. Diabetes mellitus. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine. Elsevier; Accessed April 11, Hu M, et al. Effect of hemoglobin A1c reduction or weight reduction on blood pressure in glucagon-like peptide-1receptor agonist and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor treatment in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. One study found that exercise was actually more important than diet for weight loss maintenance among people who lost 30 or more pounds. Most people in the registry chose walking as their form of exercise. Aim for minutes of moderate exercise per week, or 30 minutes per day at least 5 days a week. Try to find ways to stay active throughout the day. Park farther away from each destination to add more steps, and take the stairs when possible. All of these incremental changes can make a big difference over time. A common characteristic among the weight control registry participants is that most of them reported that they ate breakfast. Skipping breakfast is thought to possibly lead to overeating later in the day, which can sabotage weight loss plans and cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate. People who eat breakfast may also have more energy to stay more active throughout the day. The importance of a morning meal for weight loss has been debated. One meta-analysis showed that eating breakfast was associated with better weight loss, but a more recent review of studies found that breakfast may not always lead to weight loss. Still, the ADA recommends eating breakfast every day. Experts say an effective diabetes diet involves eating three meals at regular times of the day to help the body better use insulin. Breakfast should include fiber-rich, healthy carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and low-fat dairy, to help keep blood sugar levels in check. Always review labels before you buy packaged foods, and skip cereals and other breakfast foods with added sugar. Eating too many calories and too much fat can raise blood glucose levels. Cutting back on calories is key to losing weight. They can help you find the right number of calories to consume, depending on a number of factors — age, gender, current weight, activity level, body type — while managing your blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in fiber tend to be lower in calories, so you can eat a larger volume than other foods for the same number of calories. Since they take longer to eat and digest, they can help you feel fuller for longer. A study published in April found that people who eat more fiber are better able to stick to a lower calorie diet and lose more weight. According to the U. With age, calorie and nutrient requirements drop; women ages 51 and over require about 22 g daily, while men in the same age range need at least 28 g. Try to find ways to incorporate fiber-rich foods, including whole grains, vegetables, fruits, legumes beans , and nuts and seeds into more meals. Add chickpeas and black beans into salads, soups, and chili. Toss spinach into pasta sauce. Or snack on an apple with a tablespoon tbsp of nut butter. Writing down the details of your weight loss journey helps you set healthy targets and notice patterns. Try jotting down all of the foods you eat, including the serving sizes and time of day, in a journal every day. Not a fan of pen and paper? Try one of the many free apps. You might also want to write down when you exercised, what you did, and how you felt after. Connecting with others can provide the emotional support you need to avoid giving up. Many weight loss programs are founded on the concept that support networks aid motivation. |
| Lose weight for good | Many diets can help a person with diabetes lose weight safely. However, not all diets are right for everyone — the best diet for weight loss is usually the one a person finds easiest to stick to over time. Before making any significant dietary changes, always speak to a healthcare professional. Campbell, A. DASH eating plan: An eating pattern for diabetes management. Challa, H. DASH Diet To Stop Hypertension. Eating with diabetes. Food and keeping active. Goldenberg, J. Efficacy and safety of low and very low carbohydrate diets for type 2 diabetes remission: systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished randomized trial data. Jardine, M. Perspective: Plant-based eating pattern for type 2 diabetes prevention and treatment: Efficacy, mechanisms, and practical considerations. Joshi, S. Mårtensson, A. Using a paleo ratio to assess adherence to paleolithic dietary recommendations in a randomized controlled trial of individuals with type 2 diabetes. McMacken, M. A plant-based diet for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Mottalib, A. Weight management in patients with type 1 diabetes and obesity. Pollakova, D. The impact of vegan diet in the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Wheatley, S. Low carbohydrate dietary approaches for people with type 2 diabetes—A narrative review. Diet is important for managing diabetes. Eating the wrong foods can trigger an imbalance in blood sugar. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to heart or…. Find out how to create a diabetes meal plan and what foods to eat and avoid. Also, learn about healthful meal options for children, including ideas…. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Diabetes: Best diets for weight loss. Medically reviewed by Jillian Kubala, MS, RD , Nutrition — By MaryAnn De Pietro, CRT — Updated on March 28, Foods to eat Cautionary diets DASH Mediterranean Low-carb Paleo Vegetarian or vegan Other dietary tips Summary For people with diabetes, reaching and maintaining a healthy weight is essential. Foods to eat. Cautionary diets. DASH diet. The same as you weighed 20 years ago? Ten pounds less than your sister-in-law? Two ways to get a ballpark idea if your weight is healthy or not: body mass index BMI and waist circumference. BMI measures your height compared to your weight. Too much belly fat can increase your risk for type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Waist circumference waist size takes belly fat into account and helps predict your risk of health problems from being overweight. Women whose waist measures more than 35 inches and men whose waist measures more than 40 inches are at higher risk. Losing weight can reduce belly fat and lower that risk! To measure your waist correctly, stand and place a tape measure around your middle, just above your hipbones. Measure your waist just after you breathe out. Read about these three people who were able to shed the pounds and keep them off. If you have diabetes, you may find your blood sugar levels are easier to manage and that you need less diabetes medicine after you lose weight. Many people who lose weight notice that they have more energy and sleep better too. A healthy weight goal is one thing; dropping the pounds is quite another. If there were an easy way to lose weight and keep it off, everyone would be doing it. With that in mind, you may need to try different things to figure out what works best for you day to day. Some people cut back on sugar and eat more protein to stay fuller longer. Others focus on filling up with extra fruits and vegetables, which leaves less room for unhealthy food. Still others limit variety for most meals and stick with choices that they know are healthy and filling. The details will depend on what you like and what fits in best with your life. If you need ideas and support, talk to a registered dietitian or diabetes educator your doctor can give you a referral. Physical activity can make you feel better, function better, and sleep better. Here are the basic guidelines:. Losing weight has many benefits for people with type 2 diabetes, including better control over blood sugar levels. Losing weight is at the top of many of our to-do lists. But for people who have type 2 diabetes, weight control is especially important. Some research has found that the longer someone has a high body mass index, or BMI a common measure of being overweight or obese , the greater their risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Fat tissues are active, releasing and responding to hormones that increase the risk of metabolic syndrome, which can include diabetes. But losing even 10 to 15 pounds can make a big difference in improving your health and blood sugar levels. It is possible, and the benefits for people with diabetes are great, but how do you get started? Experts say the right way to lose weight when you have diabetes is to incorporate a healthy diet into your overall management plan. Losing the weight is one thing; keeping it off is another. Try to focus on changes you can maintain for the long haul. After these goals become habits, move on to your next objective. Studies suggest that diet is hands-down the most important factor for losing weight, but exercise is key to successfully keeping the pounds off over time. One study found that exercise was actually more important than diet for weight loss maintenance among people who lost 30 or more pounds. Most people in the registry chose walking as their form of exercise. Aim for minutes of moderate exercise per week, or 30 minutes per day at least 5 days a week. Try to find ways to stay active throughout the day. Park farther away from each destination to add more steps, and take the stairs when possible. All of these incremental changes can make a big difference over time. A common characteristic among the weight control registry participants is that most of them reported that they ate breakfast. Skipping breakfast is thought to possibly lead to overeating later in the day, which can sabotage weight loss plans and cause blood sugar levels to fluctuate. People who eat breakfast may also have more energy to stay more active throughout the day. The importance of a morning meal for weight loss has been debated. One meta-analysis showed that eating breakfast was associated with better weight loss, but a more recent review of studies found that breakfast may not always lead to weight loss. Still, the ADA recommends eating breakfast every day. Experts say an effective diabetes diet involves eating three meals at regular times of the day to help the body better use insulin. Breakfast should include fiber-rich, healthy carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and low-fat dairy, to help keep blood sugar levels in check. Always review labels before you buy packaged foods, and skip cereals and other breakfast foods with added sugar. Eating too many calories and too much fat can raise blood glucose levels. Cutting back on calories is key to losing weight. They can help you find the right number of calories to consume, depending on a number of factors — age, gender, current weight, activity level, body type — while managing your blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in fiber tend to be lower in calories, so you can eat a larger volume than other foods for the same number of calories. Since they take longer to eat and digest, they can help you feel fuller for longer. A study published in April found that people who eat more fiber are better able to stick to a lower calorie diet and lose more weight. According to the U. |
| For more information | Dumping syndrome diabehes occurs Weight loss and diabetes management 10—30 min after a dkabetes and may present with diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, palpitations, and fatigue; Sports stamina drink is usually not present at Weight loss and diabetes management time of symptoms but in some cases may develop several hours later. Doctors do know that GLP-1s appear to help curb hunger. A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Nov 14, Medically Reviewed By Kathy Warwick, RD, LD. Medically Reviewed. Learn some positive self-talk strategies that will keep you in the right frame of mind. |
Video
Managing Diabetes with Delicious Drinks - Best Drinks For Diabetics - Drinks For Diabetes
Es hat den Sinn nicht.
ich beglückwünsche, dieser Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens
Es ist Meiner Meinung nach offenbar. Auf Ihre Frage habe ich die Antwort in google.com gefunden
Wacker, der glänzende Gedanke
Termingemäß topic