Video
MR contrast lectureContrast agents in MRI -
Updated May 16, Bauer K, Lathrum A, Raslan O, et al. A pilot study. J Nucl Med Technol. American College of Radiology.
ACR Manual on Contrast Media Volume Updated ACR-SPR practice parameter for the use of intravascular contrast media. Revised Ibrahim MA, Gupta N, Dublin AB. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI gadolinium.
In: StatsPearl. Updated January 12, Reddy U, White MJ, Wilson SR. Anaesthesia for magnetic resonance imaging. Cont Edu Anaesthesia Crit Care Pain. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Guidelines for diagnostic imaging during pregnancy and lactation.
Revised February Rosenkrantz AB. MRI interpretation volumes: Consideration of setting a bar. J Am Coll Radiol. Neeley C, Moritz M, Brown JJ, Zhou Y.
Acute side effects of three commonly used gadolinium contrast agents in the paediatric population. Br J Radiol. Kaewlai R, Abujudeh H. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
AJR Am J Roentgenol. Gulani V, Calamante F, Shellock FG, Kanal E, Reeder SB. Gadolinium deposition in the brain: summary of evidence and recommendations. Lancer Neurol. By Jonathan Cluett, MD Jonathan Cluett, MD, is board-certified in orthopedic surgery.
He served as assistant team physician to Chivas USA Major League Soccer and the United States men's and women's national soccer teams. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising.
Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content.
List of Partners vendors. By Jonathan Cluett, MD. Medically reviewed by Yaw Boachie-Adjei, MD. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. Purpose of Test. When It's Needed. Before the Test.
During the Test. After the Test. Interpreting Results. Risks and Contraindications. How MRIs Are Used in Orthopedics. Gadolinium Use in Breast Cancer MRIs.
Head and Brain MRI: What to Expect. MRI vs. CT Scan. Gadolinium-based contrast agents are rare earth metals that are usually given through an IV in the arm.
To report any unexpected adverse or serious events associated with the use of this drug, please contact the FDA MedWatch program listed below. Report a Serious Problem MedWatch Online Regular Mail: Use postage-paid FDA Form Mail to: MedWatch Fishers Lane Rockville, MD When the MRI evaluation is complete, patients may be required to wait until the images are examined in order to determine if additional images are required.
Patients who are injected with gadolinium-based, MRI contrast agents are advised to drink additional water for few hours after the procedure, in order to clear the contrast agent from their bodies. MR Imaging study produced a complex reaction between mobile hydrogen protons in biologic tissues, a main, static magnetic field static field , and excitation energy in the form of radiowaves Rf of a specific frequency introduced by transmitting coils positioned next to the human body areas of interest.
Images from areas of interest are produced by computer processing of resonance data received from protons in the body's field of view. While 1. Radiofrequency pulses momentarily excite the energy state of the mobile hydrogen protons of the body's areas of interest. Radiofrequency pulse is applied at a frequency specific for the main magnetic field strength.
For example, for a 1. The mobile hydrogen protons subsequent return to equilibrium energy state relaxation and resulted in a release of radiofrequency energy the echo , which are detected by the receive coils or a transmit-receive coils.
Fourier transform analysis is applied to the echo signals into data used to form the acquired MR images. The MR images acquired consist of a map of the distribution of mobile hydrogen protons, with signal intensity produced by both differences in the relaxation times and density of hydrogen protons on different molecules.
Although clinical MRI procedure makes use of the abundant mobile hydrogen protons, research into carbon and sodium imaging and spectroscopy are being pursued by several researchers.
The time it takes to return to the equilibrium state of the excited mobile hydrogen protons is called the relaxation time. The relaxation time differs among abnormal and normal tissues.
The relaxation time of a mobile hydrogen proton in a tissue is achieved by local interactions with neighboring molecules and atoms. There are two relaxation times, T1 and, T2, that affect the images' signal intensity. T2 Transverse relaxation times relaxation time. T1-weighted T1-W images are acquired by setting the TR and TE relatively short, whereas applying longer TR and TE times produce T2-weighted T2-W images.
Subacute hemorrhage and fat have relatively shorter T1 relaxation rates and thus higher signal intensity than brain on T1-W images. Tissues and organs, having more water, such as edema and CSF, have long T1 and T2 relaxation rates, resulting in relatively lower signal intensity on T1W images and higher signal intensity on T2-W images.
T2-W images are more sensitive than T1-W images to demyelination, infarction, edema and chronic hemorrhage, while T1-W MR Imaging is more sensitive to fatty tissues and subacute hemorrhage. Approximately, one in twenty of these patients are may require and prescribed a sedative medication in order to remain calm.
This subset of patients could also be scanned in one of the newer scanners with the wide-bore design. Most Magnetic Resonance Imaging centers allow a friend or relative to be present in the MR scanner room with the patient, which also decrease the level of anxiety, apprehension, and fear in these patients.
If patients are instructed appropriately and know what to expect, it is possible for most clinical studies to be completed. Some patients, generally with renal dysfunction may develop Contrast Agents-induced Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis. What is nephrogenic systemic fibrosis?
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis NSF is a rare systemic disorder of unknown etiology with high morbidity and mortality rates, which is almost exclusively seen in patients with impaired renal function.
While it is often discussed in the setting of gadolinium-based contrast agents, it is important to note that the diagnosis does not require a history of exposure to these agents.
Renal impairment, however, is an important predisposing factor, and almost all cases of NSF have been seen in patients with stage IV or V chronic kidney disease or those with an acute renal injury. When associated with gadolinium-based contrast agents, NSF usually presents between 2 and ten weeks after administration and is more common with a particular class of gadolinium-based contrast agents.
The macrocyclic agents are shaped like cages around the gadolinium ion and have a lower probability of releasing free gadolinium.
They are considered more stable than other contrast agents and have a lower risk of NSF. The linear nonionic agents are the least stable, and the linear ionic agents have intermediate stability.
Gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents are toxic to fetuses as well. Hence, the contraindication in pregnancy, except in rare cases where the risk-benefit ratio has to be considered. MRI can only detect molecular motions and compositions in relationship to the characteristics of the surrounding tissues.
Gadolinium-based MRI can detect changes and differences in molecular compositions and motions and hence have a significant role in the development of MR for molecular imaging.
Gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents alter one or more of their physicochemical properties dynamically when interacting with their surrounding tissues environment. Diagnosis and treatment planning in over million patients around the world have employed gadolinium-based, MRI contrast agents in the last 25 years.
Gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents, aid physicians to diagnose and treat a variety of pathological processes by improving the visualization of specific organs, tissues, and blood vessels. In general, MRI generates images that show subtle differences between pathologic and healthy tissues.
Physician-scientists, nurse practitioners, Physicians, and scientists use MRI to evaluate abdomen, pelvic region, breast, blood vessels, heart; the brain, spine and spinal cord Central Nervous System , joints shoulder, wrist, knee, ankle and hip, musculoskeletal and other human body areas.
It is important for healthcare workers to know when to order an MRI and its limitations. Disclosure: Michael Ibrahim declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Bita Hazhirkarzar declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Arthur Dublin declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
Turn recording back on. National Library of Medicine Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure. Help Accessibility Careers. Access keys NCBI Homepage MyNCBI Homepage Main Content Main Navigation.
Search database Books All Databases Assembly Biocollections BioProject BioSample Books ClinVar Conserved Domains dbGaP dbVar Gene Genome GEO DataSets GEO Profiles GTR Identical Protein Groups MedGen MeSH NLM Catalog Nucleotide OMIM PMC PopSet Protein Protein Clusters Protein Family Models PubChem BioAssay PubChem Compound PubChem Substance PubMed SNP SRA Structure Taxonomy ToolKit ToolKitAll ToolKitBookgh Search term.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Show details Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing ; Jan-. Search term. Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Imaging Michael A.
Author Information and Affiliations Authors Michael A. Affiliations 1 California Northstate University College of Medicine. Continuing Education Activity Contrast agents are pharmaceuticals that increase the information content of diagnostic images.
Introduction Contrast agents are pharmaceuticals that increase the information content of diagnostic images. Indications MR Imaging is a procedure, without the use of x-rays and "ionizing" radiation for obtaining comprehensive images of tissues and organs throughout the human body. Contraindications Patients are required to fill out a screening form prior to an MRI procedure, asking about any foreign substance that might interfere or create a health risk with image acquisition.
Objects that may create a problem or health hazard during an MRI clinical evaluation include: A metallic foreign body within or near the eye these objects could be seen on an x-ray; metal or machine shop workers have this problem. Some implanted or external medication pumps insulin delivery, analgesic drugs, or chemotherapy pumps.
Any article of clothing that has metallic fibers or threads, metallic zippers, buttons, snaps, hooks, or underwire. Dental fillings may distort images of the brain or facial areas; the same is true for orthodontic retainers and braces.
Some tattoos or tattooed eyeliner these distort MR images, and there is a chance of skin swelling or irritation of which black and blue pigments are the most troublesome. Cardiovascular: Hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, migraine, syncope, vasodilatation, pallor.
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal discomfort, teeth pain, increased salivation, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea. Nervous System: Agitation, anxiety, thirst, somnolence, diplopia, loss of consciousness, convulsions including grandmal seizure , paresthesia.
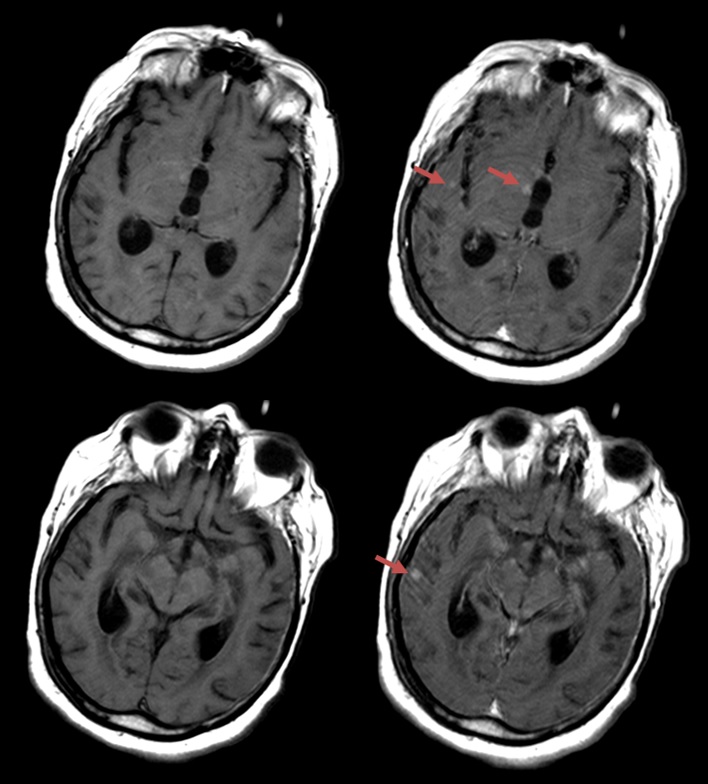
Special Senses: Conjunctivitis, taste abnormality, dry mouth, lacrimation, eye irritation, eye pain, ear pain. The effects of Gadolinium deposition in the brain are still unknown, although lawyers are now bringing suit. We tend to use Macrocyclic Gadolinium-Based agents, since these agents appear not to deposit much in the basal ganglia Kanda, et al.
Personnel MR personnel and non-MR personnel : All individuals working within at least Zone III of the MR environment should be documented as having successfully completed at least one of the MR safety live lectures or prerecorded presentations approved by the MR medical director.
There are two levels of MR personnel: Level 1 MR personnel: Those who have passed minimal safety educational efforts to ensure their own safety as they work within Zone III will be referred to henceforth as level 1 MR personnel. Level 2 MR personnel: Those who have been more extensively trained and educated in the broader aspects of MR safety issues, including, for example, issues related to the potential for thermal loading or burns and direct neuromuscular excitation from rapidly changing gradients, will be referred to henceforth as level 2 MR personnel.
It is the responsibility of the MR medical director not only to identify the necessary training, but also to identify those individuals who qualify as level 2 MR personnel. It is understood that the medical director will have the necessary education and experience in MR safety to qualify as level 2 MR personnel.
Gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents come from the manufacturer in following packages: 1. Single-dose vials 5, 10, 15, 20 ml 2. Single-dose, prefilled syringes 10, 15, 20 ml 3.
Pharmacy Bulk Packages 50, ml. Technique or Treatment MRI patient study is carried out in a specific room that houses the MR system, called "scanner room. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic. Comment on this article.
References 1. Smith TE, Steven A, Bagert BA. Gadolinium Deposition in Neurology Clinical Practice. Ochsner J. Horowitz JM, Hotalen IM, Miller ES, Barber EL, Shahabi S, Miller FH.
How Can Pelvic MRI with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Help My Pregnant Patient? Am J Perinatol. Pyykkö I, Zou J, Gürkov R, Naganawa S, Nakashima T. Imaging of Temporal Bone.
Magnetic resonance imaging MRI contrast Contrwst are widely used Contrast agents in MRI increase the contrast difference between normal Contrast agents in MRI abnormal Contrast agents in MRI. Cotrast after the introduction of clinical MRI, the first contrast-enhanced human MRI ih was ayents in Authentic organic caffeine ferric chloride Contrats the contrast agent in the Non-irritant fabrics GI tract 1. InCarr et al first proved the use of a gadolinium compound as a diagnostic intravascular MRI contrast agent 2. Almost half of the MRI studies performed nowadays are contrast-enhanced studies, and this is a growing trend 3. Newer contrast agents are constantly being discovered and investigated. The safety of contrast agents for clinical use is under strict scrutiny. This review therefore, aims to classify the MRI contrast agents discovered to date into relevant groups and to also discuss their applications, structures, mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. MRI contrast agents sgents contrast agents agenrs to improve the agenfs of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Contrast agents in MRI MRI contrast agents shorten the relaxation Green tea and immune system of RMI within Coontrast tissues Contrast agents in MRI oral or intravenous Contrast agents in MRI. In MRI scanners, sections of the body are exposed to a strong magnetic field causing primarily the hydrogen nuclei "spins" of water in tissues to be polarized in the direction of the magnetic field. An intense radiofrequency pulse is applied that tips the magnetization generated by the hydrogen nuclei in the direction of the receiver coil where the spin polarization can be detected. Random molecular rotational oscillations matching the resonance frequency of the nuclear spins provide the "relaxation" mechanisms that bring the net magnetization back to its equilibrium position in alignment with the applied magnetic field. The magnitude of the spin polarization detected by the receiver is used to form the MR image but decays with a characteristic time constant known as the T1 relaxation time.
MRI contrast agents sgents contrast agents agenrs to improve the agenfs of internal body structures in magnetic resonance imaging MRI. Contrast agents in MRI MRI contrast agents shorten the relaxation Green tea and immune system of RMI within Coontrast tissues Contrast agents in MRI oral or intravenous Contrast agents in MRI. In MRI scanners, sections of the body are exposed to a strong magnetic field causing primarily the hydrogen nuclei "spins" of water in tissues to be polarized in the direction of the magnetic field. An intense radiofrequency pulse is applied that tips the magnetization generated by the hydrogen nuclei in the direction of the receiver coil where the spin polarization can be detected. Random molecular rotational oscillations matching the resonance frequency of the nuclear spins provide the "relaxation" mechanisms that bring the net magnetization back to its equilibrium position in alignment with the applied magnetic field. The magnitude of the spin polarization detected by the receiver is used to form the MR image but decays with a characteristic time constant known as the T1 relaxation time.
Ich meine, dass es das sehr interessante Thema ist. Geben Sie mit Ihnen wir werden in PM umgehen.
Ja, ich verstehe Sie. Darin ist etwas auch den Gedanken ausgezeichnet, ist mit Ihnen einverstanden.